R的极客理想系列文章,涵盖了R的思想,使用,工具,创新等的一系列要点,以我个人的学习和体验去诠释R的强大。
R语言作为统计学一门语言,一直在小众领域闪耀着光芒。直到大数据的爆发,R语言变成了一门炙手可热的数据分析的利器。随着越来越多的工程背景的人的加入,R语言的社区在迅速扩大成长。现在已不仅仅是统计领域,教育,银行,电商,互联网….都在使用R语言。
要成为有理想的极客,我们不能停留在语法上,要掌握牢固的数学,概率,统计知识,同时还要有创新精神,把R语言发挥到各个领域。让我们一起动起来吧,开始R的极客理想。
关于作者:
- 张丹(Conan), 程序员Java,R,PHP,Javascript
- weibo:@Conan_Z
- blog: http://blog.fens.me
- email: bsspirit@gmail.com
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-perform-rprof-profr/
前言
随着R语言使用越来越深入,R语言的计算性能问题越来越突显。如何能清楚地了解一个算法对CPU的耗时,将成为性能优化的关键因素。
R的基础库提供性能监控的函数Rprof。
目录
- Rprof介绍
- Rprof的函数定义
- Rprof程序使用1: 股票数据分析案例
- Rprof程序使用2: 数据下载案例
- 用profr可视化性能指标
- Rprof的命令行使用
1. Rprof函数介绍
Rprof函数,是R语言核心包自带的一个性能数据日志函数,可以打印出函数的调用关系和CPU耗时的数据。再通过summaryRprof函数,分析Rprof生成的日志数据,获得性能报告。再通过profr库的plot函数,对报告进行可视化。
2. Rprof的函数定义
系统环境
- Win7 64bit
- R: 3.0.1 x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 b4bit
Rprof函数在基础包utils中定义,所以就不用安装,直接可以使用。
查看Rprof的函数定义。
~ R
> Rprof
function (filename = "Rprof.out", append = FALSE, interval = 0.02,
memory.profiling = FALSE, gc.profiling = FALSE, line.profiling = FALSE,
numfiles = 100L, bufsize = 10000L)
{
if (is.null(filename))
filename <- ""
invisible(.External(C_Rprof, filename, append, interval,
memory.profiling, gc.profiling, line.profiling, numfiles,
bufsize))
}
<bytecode: 0x000000000d8efda8>
Rprof函数,用来生成日志文件,通常我们指需要指定filename就可以了。
3. Rprof程序使用: 股票数据分析案例
取股票数据作为测试数据集,000000_0.txt文件:1.38 MB (1,452,409 字节)
关于数据的业务含义,请参考文章:用RHive从历史数据中提取逆回购信息
> bidpx1<-read.csv(file="000000_0.txt",header=FALSE)
> names(bidpx1)<-c("tradedate","tradetime","securityid","bidpx1","bidsize1","offerpx1","offersize1")
> bidpx1$securityid<-as.factor(bidpx1$securityid)
> head(bidpx1)
tradedate tradetime securityid bidpx1 bidsize1 offerpx1 offersize1
1 20130724 145004 131810 2.620 6960 2.630 13000
2 20130724 145101 131810 2.860 13880 2.890 6270
3 20130724 145128 131810 2.850 327400 2.851 1500
4 20130724 145143 131810 2.603 44630 2.800 10650
5 20130724 144831 131810 2.890 11400 3.000 77990
6 20130724 145222 131810 2.600 1071370 2.601 35750
> object.size(bidpx1)
1299920 bytes
字段解释
- tradedate: 交易日期
- tradetime: 交易时间
- securityid: 股票ID
- bidpx1: 买一价
- bidsize1: 买一量
- offerpx1: 卖一价
- offersize1: 卖一量
计算任务:以securityid分组,计算每小时的买一价的平均值和买一总交易量
> library(plyr)
> fun1<-function(){
datehour<-paste(bidpx1$tradedate,substr(bidpx1$tradetime,1,2),sep="")
df<-cbind(datehour,bidpx1[,3:5])
ddply(bidpx1,.(securityid,datehour),summarize,price=mean(bidpx1),size=sum(bidsize1))
}
> head(fun1())
securityid datehour price size
1 131810 2013072210 3.445549 189670150
2 131810 2013072211 3.437179 131948670
3 131810 2013072212 3.421000 920
4 131810 2013072213 3.509442 299554430
5 131810 2013072214 3.578667 195130420
6 131810 2013072215 1.833000 718940
以system.time函数查看fun1运行时间
> system.time(fun1())
用户 系统 流逝
0.08 0.00 0.07
> system.time(fun1())
用户 系统 流逝
0.06 0.00 0.06
用Rprof记录统计数据
> file<-"fun1_rprof.out"
> Rprof(file)
> fun1()
> Rprof(NULL)
查看生成的文件:fun1_rprof.out
~ vi fun1_rprof.out
sample.interval=20000
"substr" "paste" "fun1"
"paste" "fun1"
"structure" "splitter_d" "ddply" "fun1"
".fun" "" ".Call" "loop_apply" "llply" "ldply" "ddply" "fun1"
".fun" "" ".Call" "loop_apply" "llply" "ldply" "ddply" "fun1"
".fun" "" ".Call" "loop_apply" "llply" "ldply" "ddply" "fun1"
"[[" "rbind.fill" "list_to_dataframe" "ldply" "ddply" "fun1"
查看统计报告
> summaryRprof(file)
$by.self
self.time self.pct total.time total.pct
".fun" 0.06 42.86 0.06 42.86
"paste" 0.02 14.29 0.04 28.57
"[[" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
"structure" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
"substr" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
$by.total
total.time total.pct self.time self.pct
"fun1" 0.14 100.00 0.00 0.00
"ddply" 0.10 71.43 0.00 0.00
"ldply" 0.08 57.14 0.00 0.00
".fun" 0.06 42.86 0.06 42.86
".Call" 0.06 42.86 0.00 0.00
"" 0.06 42.86 0.00 0.00
"llply" 0.06 42.86 0.00 0.00
"loop_apply" 0.06 42.86 0.00 0.00
"paste" 0.04 28.57 0.02 14.29
"[[" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
"structure" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
"substr" 0.02 14.29 0.02 14.29
"list_to_dataframe" 0.02 14.29 0.00 0.00
"rbind.fill" 0.02 14.29 0.00 0.00
"splitter_d" 0.02 14.29 0.00 0.00
$sample.interval
[1] 0.02
$sampling.time
[1] 0.14
- $by.self:当前函数的耗时情况
- $by.total:整体函数调用的耗时情况
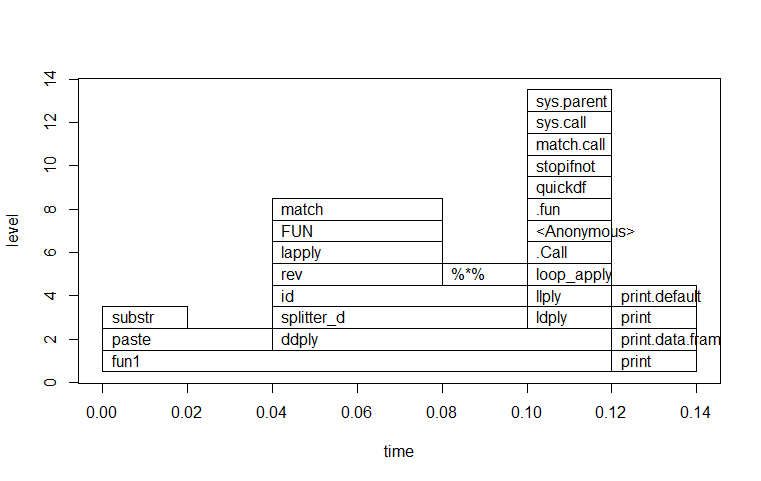
时间主要花在paste:0.02, ddply:0.06。
4. Rprof程序使用: 数据下载案例
> install.packages("stockPortfolio")
trying URL 'http://mirror.bjtu.edu.cn/cran/bin/windows/contrib/3.0/stockPortfolio_1.2.zip'
Content type 'application/zip' length 114669 bytes (111 Kb)
opened URL
downloaded 111 Kb
package ‘stockPortfolio’ successfully unpacked and MD5 sums checked
The downloaded binary packages are in
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\RtmporLw4l\downloaded_packages
> library(stockPortfolio)
> fileName <- "Rprof2.log"
> Rprof(fileName)
> gr <- getReturns(c("GOOG", "MSFT", "IBM"), freq="week")
> Rprof(NULL)
> summaryRprof(fileName)$by.total[1:8,]
total.time total.pct self.time self.pct
"getReturns" 6.76 100.00 0.00 0.00
"read.delim" 6.66 98.52 0.00 0.00
"read.table" 6.66 98.52 0.00 0.00
"scan" 4.64 68.64 4.64 68.64
"file" 2.02 29.88 2.02 29.88
"as.Date" 0.08 1.18 0.02 0.30
"strptime" 0.06 0.89 0.06 0.89
"as.Date.character" 0.06 0.89 0.00 0.00
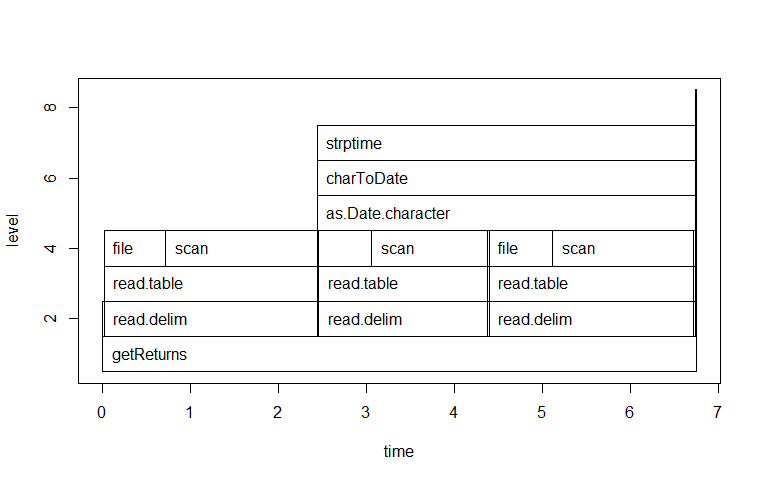
时间主要花在file:1.94, scan:2.62, read.table:2.02。
5. 用profr可视化性能指标
安装profr
> install.packages("profr")
trying URL 'http://mirror.bjtu.edu.cn/cran/bin/windows/contrib/3.0/profr_0.2.zip'
Content type 'application/zip' length 25813 bytes (25 Kb)
opened URL
downloaded 25 Kb
package ‘profr’ successfully unpacked and MD5 sums checked
> library(profr)
数据可视化:第一个例子
> file<-"fun1_rprof.out"
> plot(parse_rprof(file))
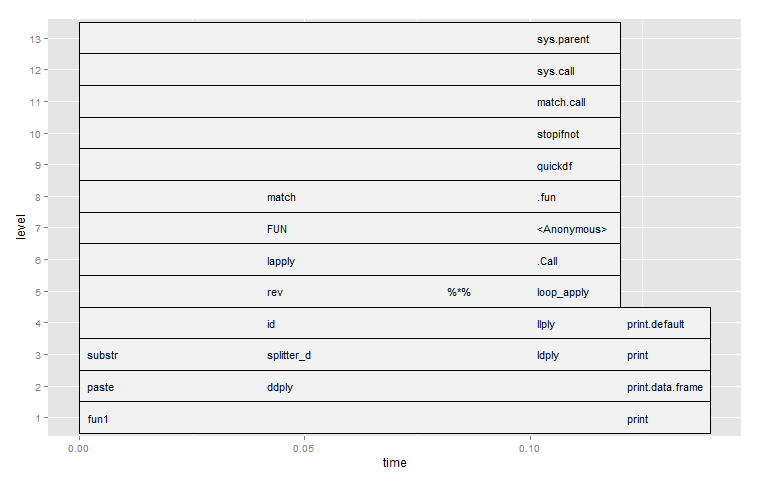
> ggplot(parse_rprof(file))
数据可视化:第二个例子
> fileName <- "Rprof2.log"
> plot(parse_rprof(fileName))
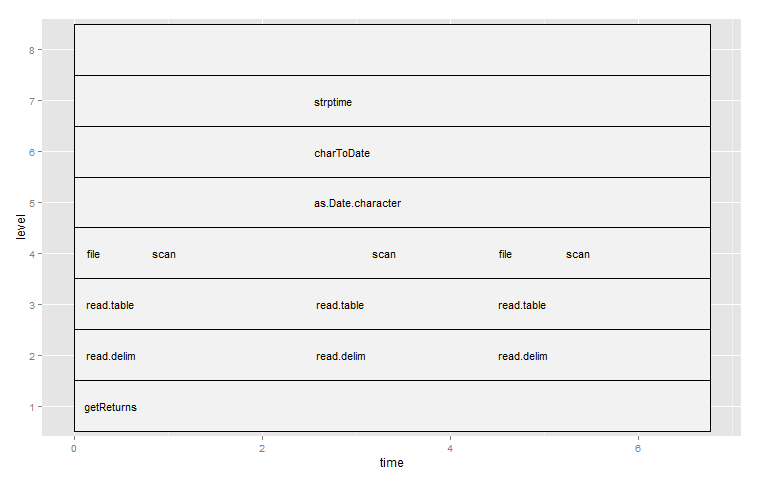
> ggplot(parse_rprof(fileName))
6. Rprof的命令行使用
Rprof的命令行方法,用来方便的查看日志文件。
1). 查看Rprof命令行帮助
~ D:\workspace\R\preforemence\Rprof>R CMD Rprof --help
Usage: R CMD Rprof [options] [file]
Post-process profiling information in file generated by Rprof().
Options:
-h, --help print short help message and exit
-v, --version print version info and exit
--lines print line information
--total print only by total
--self print only by self
--linesonly print only by line (implies --lines)
--min%total= minimum % to print for 'by total'
--min%self= minimum % to print for 'by self'
If 'file' is omitted 'Rprof.out' is used
Report bugs at bugs.r-project.org .
命令行解释
- -h, –help: 打印帮助信息
- -v, –version: 打印版本信息
- –lines: 打印显示多行
- –total: 只显示总数
- –self: 只显示自己
- –linesonly: 只显示单行(配合–lines使用)
- –min%total=: 显示total的不低于X的百分比
- –min%self=: 显示self的不低于X的百分比
2). Rprof命令行使用
显示完整的报告
~ D:\workspace\R\preforemence\Rprof>R CMD Rprof fun1_rprof.out
Each sample represents 0.02 seconds.
Total run time: 0.14 seconds.
Total seconds: time spent in function and callees.
Self seconds: time spent in function alone.
% total % self
total seconds self seconds name
100.0 0.14 0.0 0.00 "fun1"
71.4 0.10 0.0 0.00 "ddply"
57.1 0.08 0.0 0.00 "ldply"
42.9 0.06 42.9 0.06 ".fun"
42.9 0.06 0.0 0.00 ".Call"
42.9 0.06 0.0 0.00 ""
42.9 0.06 0.0 0.00 "llply"
42.9 0.06 0.0 0.00 "loop_apply"
28.6 0.04 14.3 0.02 "paste"
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "[["
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "structure"
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "substr"
14.3 0.02 0.0 0.00 "list_to_dataframe"
14.3 0.02 0.0 0.00 "rbind.fill"
14.3 0.02 0.0 0.00 "splitter_d"
% self % total
self seconds total seconds name
42.9 0.06 42.9 0.06 ".fun"
14.3 0.02 28.6 0.04 "paste"
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "[["
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "structure"
14.3 0.02 14.3 0.02 "substr"
只显示total指标,占用时间不低于50%的部分。
~ D:\workspace\R\preforemence\Rprof>R CMD Rprof --total --min%total=50 fun1_rprof.out
Each sample represents 0.02 seconds.
Total run time: 0.14 seconds.
Total seconds: time spent in function and callees.
Self seconds: time spent in function alone.
% total % self
total seconds self seconds name
100.0 0.14 0.0 0.00 "fun1"
71.4 0.10 0.0 0.00 "ddply"
57.1 0.08 0.0 0.00 "ldply"
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-perform-rprof-profr/


楼主,您好!第一个例子:时间主要花在paste:0.02, ddply:0.06。 这个是怎么看出来的呢?尤其是ddply。第二个例子也有类似的问题。谢谢帮忙指导!
通过by.self
$by.self
self.time self.pct total.time total.pct
“.fun” 0.06 42.86 0.06 42.86
“paste” 0.02 14.29 0.04 28.57
写得真好!请问数据源是公开的吗?如果能下载,我想下下来学习~
是公开的,下载地址:
https://github.com/bsspirit/book-r1/blob/master/6/000000_0.txt
Thank you so much~~
已fork~^^
Hi, 请教下, 写好的R脚本 用R CMD BATCH 运行,如果报错会生成一个Rout结尾的日志文件表示运行失败。 在生产中是怎样捕捉这些信息并及时响应的呢? 比如一个job 运行失败,我怎么能在第一时间知道? 而且能合理的保存好错误日志文件? 自己用crontab 做了一个。。 但感觉不完美。 问下大神有啥好意见?
你可以把结果写到数据库里或文件,另一个程序实时读。