算法为王系列文章,涵盖了计算机算法,数据挖掘(机器学习)算法,统计算法,金融算法等的多种跨学科算法组合。在大数据时代的背景下,算法已经成为了金字塔顶的明星。一个好的算法可以创造一个伟大帝国,就像Google。
算法为王的时代正式到来….
关于作者:
- 张丹, 分析师/程序员/Quant: R,Java,Nodejs
- blog: http://blog.fens.me
- email: bsspirit@gmail.com
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-coivd19-beijing
前言
新冠疫情已经持续三年了,前段时间在北京和上海两个超大城市爆发,一度让工作和生活陷入恐慌。当时居家办公,每天核酸,都已经变成了生活的常态。
北京疫情从4月底爆发到,到5月全面严格管控,再到6月复工复产,虽然我们都亲身经历了,但并不知道为什么北京的政策是有效的。回顾一下,让数据说话,看看我们到底我们经历了什么。
由于本人非传染病专业,文中关于传染病的专业内容大都从网上汇集和再整理,当出现本文描述与教课书不符时,请以专业教材为准。
目录
- 获取北京新冠疫情数据
- R0基本传染数介绍
- 用SIR模拟北京疫情,结果失真
- 用SIR拟合算出R0,结果合理
1. 获取北京新冠疫情数据
在全球抗击新冠肺炎疫情的过程中,传染病动力学模型发挥了巨大的作用。传染病动模型,根据传染病的传播速度不同,空间范围各异,传播途径多样,动力学机理等各种因素,对传染病模型按照传染病的类型划分为 SI,SIR,SIRS,SEIR 模型。
首先,安装nCov2019,加载nCov2019包,再加载数据。关于nCov2019包的具体安装和使用,请参考文章:用R语言获取全球新冠疫情数据
# 设置工作路径
> setwd("C:/work/R/covid19")
# 如果没安装,请先安装nCov2019包
> #remotes::install_github("YuLab-SMU/nCov2019")
# 加载nCov2019包
> library(nCov2019)
# 下载最近数据
> x <- query()
Querying the latest data...
last update: 2022-07-05
Querying the global data...
Gloabl total 555324897 cases; and 6362663 deaths
Gloabl total affect country or areas: 230
Gloabl total recovered cases: 165929
last update: 2022-07-05
Querying the historical data...
Querying the vaccine data...
Total Candidates Programs : 51
Querying the therapeutics data...
Total Candidates Programs : 84
Query finish, each time you can launch query() to reflash the data
加载其他数据处理R包,并定义公共画图函数。Y轴做了log10的转化处理。
> library(ggplot2)
> library(magrittr)
> library(reshape2)
>
> # 画图函数
> draw<-function(df){
+ dat<-melt(df,id.vars = c("date"))
+ g<-ggplot(data = dat, mapping = aes(x=date,y=value,colour=variable))
+ g<-g+geom_line() + geom_point()
+ g<-g+scale_y_log10()
+ g<-g+ggtitle("北京疫情统计")+xlab("日期")+ylab("Log(人数)")
+ g
+ }
获取中国北京的新冠数据。
> hist<-x$historical
> beijing<-hist["China","beijing"]
# 查看数据集
> head(beijing)
country province date cases deaths recovered
6 China beijing 2020-01-22 14 0 0
95 China beijing 2020-01-23 22 0 0
184 China beijing 2020-01-24 36 0 1
273 China beijing 2020-01-25 41 0 2
362 China beijing 2020-01-26 68 0 2
451 China beijing 2020-01-27 80 1 2
计算每日新增数据,并画图展示北京整体疫情的情况。
> beijing$daily<-c(0,diff(beijing$cases))
# 画图
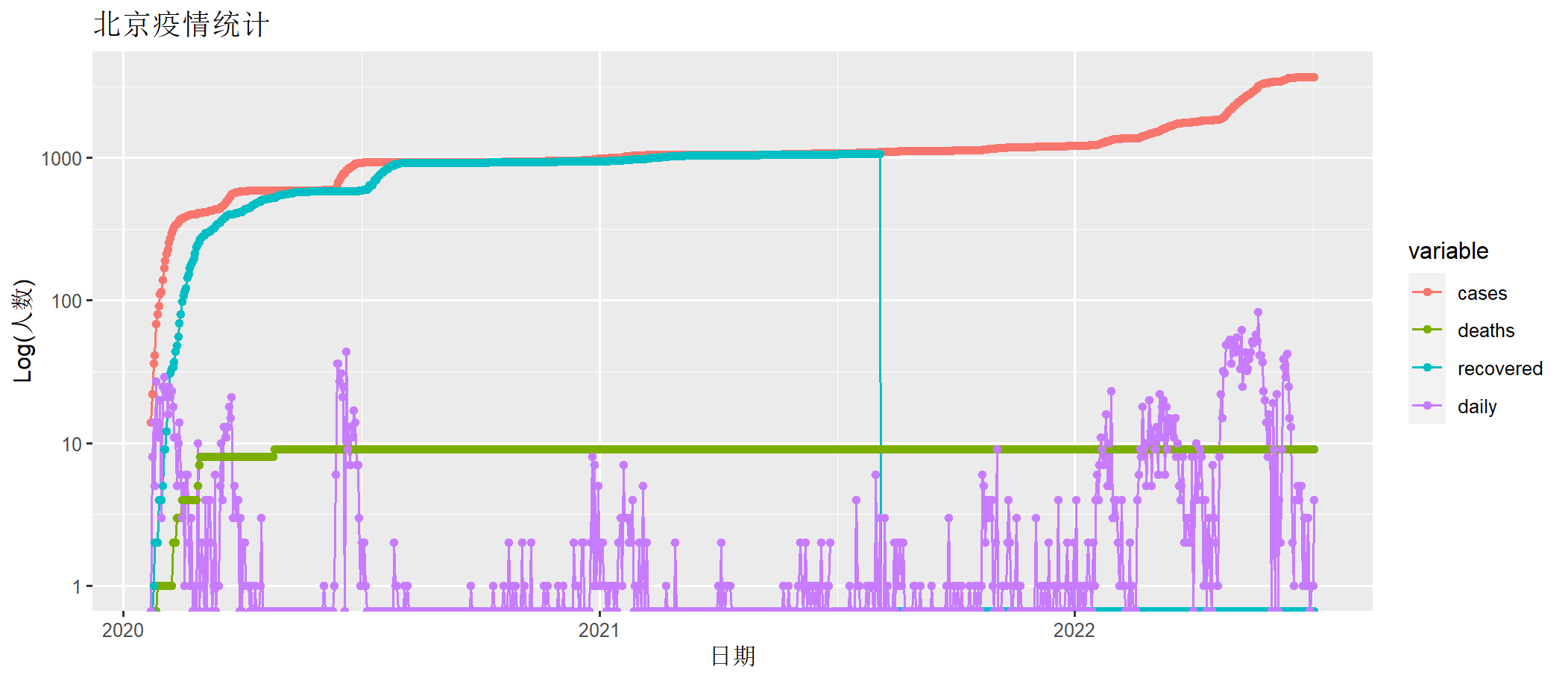
> draw(beijing[,c("date", "cases" ,"deaths", "recovered","daily")])
上图中cases为确诊人数,deaths为死亡人数,recovered为治愈人数(治愈后不会再得),daily为每日新增确诊人数。x轴为时间日期,y轴为人数(log化的人数)。
本次北京的疫情,从4月开始爆发,到6月基本控制住了。我们截取取从4月1日到7月4日数据,进行分析。
# 取2022-04-01开始到2022-07-04数据
> bj202204<-beijing[which(beijing$date>=as.Date("2022-04-01")),]
> head(bj202204)
country province date cases deaths recovered daily
71206 China beijing 2022-04-01 1777 9 0 8
71295 China beijing 2022-04-02 1777 9 0 0
71384 China beijing 2022-04-03 1781 9 0 4
71473 China beijing 2022-04-04 1791 9 0 10
71562 China beijing 2022-04-05 1795 9 0 4
71651 China beijing 2022-04-06 1800 9 0 5
# 计算这段时间的累计确诊数量
> bj202204$cum<-cumsum(bj202204$daily)
# 画图
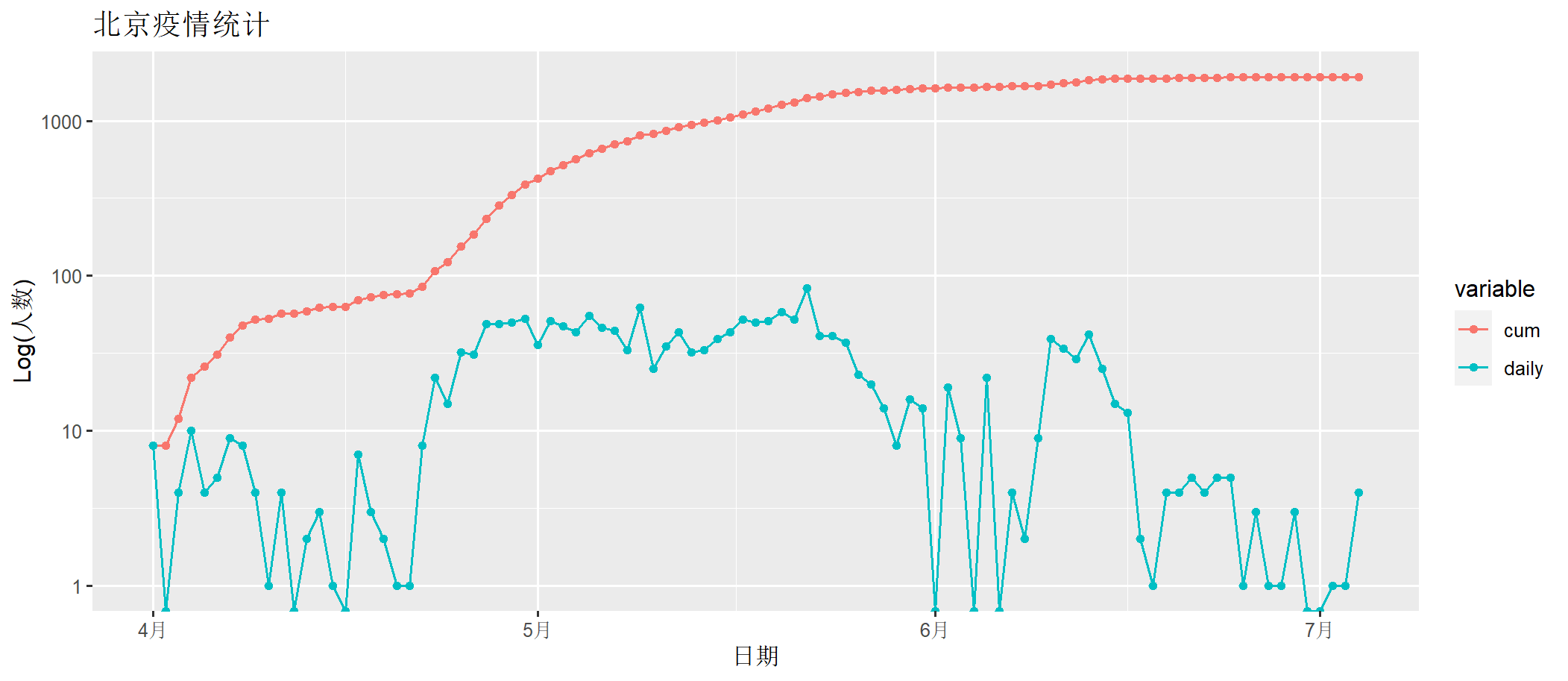
> draw(bj202204[,c("date", "cum","daily")])
上图中, daily为每日确诊数量,cum为累计确诊数量。x轴为时间日期,y轴为人数(log化的人数)。
2. R0基本传染数和Re有效传染数
在有了数据后,我们接下来要先了解一下R0基本传染数的概念,后面在用传染病动力学模型做拟合时,就可以用来对实际的疫情进行评价。
2.1 R0基本传染数
R0基本传染数,这是一个很重要的传染病学概念,用来衡量病原体的传染性。R0是指在一个完全易感人群中(没有任何预防手段介入并且所有人对此病原体没有免疫力的情况下),一个病例能传染的平均人数。
R0最常用的方法是使用累积发病率数据。
R0 = 传染期 * 每人每天的接触者数 * 每个接触者的感染概率- 若R0 < 1,意味着在没有防控的情况下, 一个感染者将传给少于一个人,所以传染病将会自行逐渐消失。
- 若R0 > 1,每个感染者能传染多于一个人,那么就会有发展成流行病(epidemic)的可能性。但是一般不会永远持续,因为可能被感染的人口会慢慢减少。部分人口可以死该传染病,部分则可能治愈后产生免疫力。
- 若R0 = 1,传染力维持,病院持续存在,会变成地方性流行病。
但R0不代表当前被感染的总人数。它也不是疾病严重程度的衡量指标。它只表示一个感染者平均能感染几个人,而不是告诉我们这些感染者疾病的严重程度。
对于一个特定的传染病,R0不一定是恒定的,它可能取决于人口密度和接触方式等因素。尽管如此,对于不同人群,一个特定传染病的R0是相对相似的。
部分传染病的R0值,数据来源 https://zh.m.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/基本传染数
| 疾病 | 传播途径 | R0 |
|---|---|---|
| 麻疹 | 空气传播 | 12-18 |
| 白喉 | 唾液 | 6-7 |
| 天花 | 空气传播、 飞沫传播 | 5-7 |
| 脊髓灰质炎 | 粪口传播 | 5-7 |
| 风疹 | 空气传播、 飞沫传播 | 5-7 |
| 流行性腮腺炎 | 呼吸道飞沫 | 10-12 |
| HIV/AIDS | 性传播 | 4.5 |
| 百日咳 | 空气传播、 飞沫传播 | 5.5 |
| SARS | 空气传播、 飞沫传播、粪口传播 | 2-5 |
| 流行性感冒(1918年流感大流行) | 空气传播、 飞沫传播 | 2-3 |
| 埃博拉出血热(西非埃博拉病毒疫症) | 体液传播 | 1.5-2.5 |
| COVID-19 | 飞沫传播、接触传播、粪口传播 | 1.4-3.8 3.8–8.9(截至2020年6月) Delta变异株:5.1 Alpha变异株:4–5 Omicron变异株:7 |
| 中东呼吸综合征 | 呼吸道飞沫 | 0.5 (0.3 –0.8 ) |
| 普通感冒 | 呼吸道飞沫 | 2–3 |
| 水痘 | 空气传播疾病 | 10–12 |
有了上面的不同传染病的比较级,就能对本次新冠疫情有了一个数量上的感觉,Omicron变异株:7的数值,确实是非常高的传染性。
2.2 Re有效传染数
相对于R0,另一个指标Re可以帮我们分析,如何抑制疫情的爆发。Re为有效传染数,是指一个群体在任何特定的时间,不完全易感或已采取适当防控措施的情况下,单例病例能感染的平均人数。随着人口越来越多地获得免疫,无论是通过感染或接种疫苗后的个体免疫,还是随着人们的死亡,它都会发生变化。
Re = R0 *(1 – 有效控制率)*(易感人群比例)
- 当Re>1时,每个受感染的个体将疾病传播给不止一个人,疾病可能在人群中传播。
- 当Re<1时,可能会发生个体病例传播给另一个人发生新的感染,要遏制疾病流行,Re必须小于1,疫苗通过减少易感人群的比例,是使Re < 1的最佳手段。
3. 用SIR模型模拟北京疫情
我们首先用SIR模型进行北京疫情的模拟,具体操作,使用确定的SIR公式,通过设置参数带入模型模拟本次疫情的情况,观察SIR模型模拟的数据是否与实际发生的确诊数据,是否是匹配的。
我们直接使用EpiModel包,自带的SIR模型进行拟合。关于EpiModel包的详细使用介绍,请参考文章 EpiModel快速上手传染病模型。
R程序实现代码
> library(EpiModel)
> param <- param.dcm(inf.prob = 0.5, act.rate = 0.5, rec.rate = 1/7)
> init <- init.dcm(s.num = 30*1000*1000, i.num = 8, r.num = 0)
> control <- control.dcm(type = "SIR", nsteps = 200, dt = 0.5)
> mod <- dcm(param, init, control)
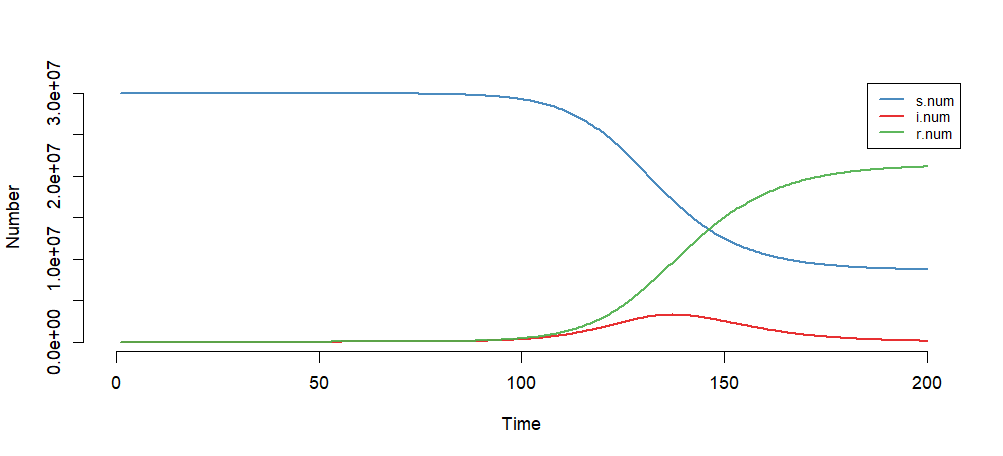
设置模型初始参数:日感染率inf.prob=0.5,日传播率 act.rate=0.5,恢复率rec.rate=1/7。易感染者s.num=30*1000*1000,为北京人口数量,已感染者i.num=0,治愈r.num=0,观察周期nsteps=200。
> mod
EpiModel Simulation
=======================
Model class: dcm
Simulation Summary
-----------------------
Model type: SIR
No. runs: 1
No. time steps: 200
No. groups: 1
Model Parameters
-----------------------
inf.prob = 0.5
act.rate = 0.5
rec.rate = 0.1428571
Model Output
-----------------------
Variables: s.num i.num r.num si.flow ir.flow num
模型模拟结果
> plot(mod)
把实际的北京确诊数据,与模拟的确认数据画到一起。
# 生成日期列
> moddf<-as.data.frame(mod)
> moddf$date<-as.Date("2022-04-01")+0:(nrow(moddf)-1)
# 合并数据集
> d1<-data.frame(date=moddf$date,i=moddf$i.num,variable="sir")
> d2<-data.frame(date=bj202204$date,i=bj202204$cum,variable="real")
> mdf<-rbind(d1,d2)
# 画图
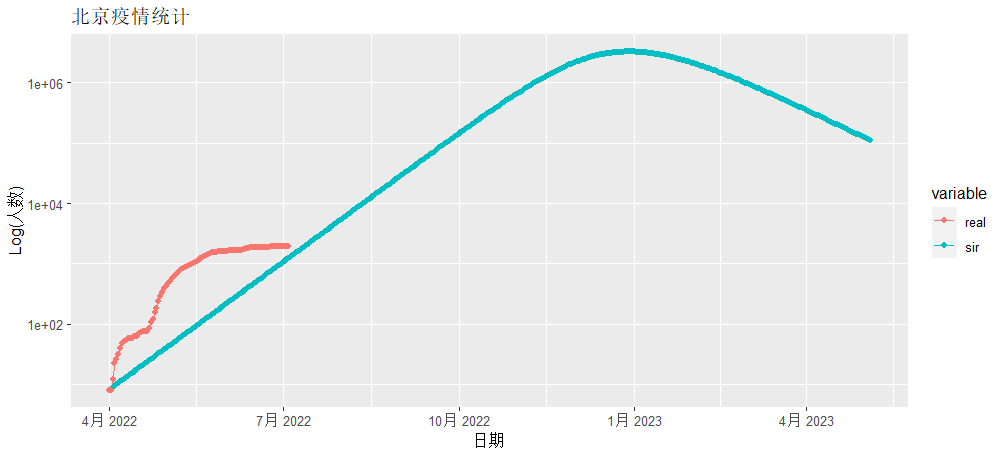
> g<-ggplot(data = mdf, mapping = aes(x=date,y=i,colour=variable))
> g<-g+geom_line() + geom_point()
> g<-g+scale_y_log10()
> g<-g+ggtitle("北京疫情统计")+xlab("日期")+ylab("Log(人数)")
> g
红色为北京实际发生确诊的数据,蓝色线为SIR模型模拟的数据,从图中看是有很大的差异性的,所以直接用确定性的公式做疫情的模拟是很不靠谱的。
4. 基于 SIR 拟合北京疫情
使用SIR模型进行拟合,并设置运行参数
# 加载程序包
> library(lubridate)
> library(plyr)
# 设置初始化参数
> cases <- bj202204$cum # 每日累计
> N <- 30*1000*1000 # 总人数
> startDay <- 6 # 开始累计时间
# 计算每日累计确诊
> infected <- cases[startDay:length(cases)]
> infected
[1] 31 40 48 52 53 57 57 59 62 63 63 70 73 75 76 77 85 107 122 154
[21] 185 234 283 333 386 422 473 520 563 618 664 708 741 803 828 863 906 938 971 1010
[41] 1053 1105 1155 1206 1264 1316 1399 1440 1481 1518 1541 1561 1575 1583 1599 1613 1613 1632 1641 1641
[61] 1663 1663 1667 1669 1678 1717 1751 1780 1822 1847 1862 1875 1877 1878 1882 1886 1891 1895 1900 1905
[81] 1906 1909 1910 1911 1914 1914 1914 1915 1916 1920
# 以多少天为窗口计算R0
> window <- 12
定义SIR模型的拟合函数,用来进行后面的数据拟合。SIR模型的计算公式详解,请参考文章:用R语言解读传染病模型
# 定义SIR模型的拟合函数
> SIR<-function(time,vars,params){
+ with(as.list(c(vars,params)),{ #beta=rio,gamma=mu
+ num <- s.num + i.num + r.num
+ dS<- -beta * i.num * s.num/num
+ dI<- beta * i.num * s.num/num - gamma * i.num
+ dR<- gamma * i.num
+ return(list(c(dS,dI,dR)))
+ })
+ }
这里没有直接使用EpiModel包的SIR函数的原因是,EpiModel的参数命名规则不太一样,另外需要设置额外的参数,在这里用不上,比如inf.prob、act.rate等。当然如果一定用EpiModel的SIR函数,可以使用mod_SI_1g_cl(t, t0, parms)函数,自己做一下适配,并不复杂。
# 查看mod_SIR_1g_cl函数定义
> mod_SIR_1g_cl
function (t, t0, parms)
{
with(as.list(c(t0, parms)), {
num <- s.num + i.num + r.num
lambda <- inf.prob * act.rate * i.num/num
if (!is.null(parms$inter.eff) && t >= inter.start) {
lambda <- lambda * (1 - inter.eff)
}
si.flow <- lambda * s.num
ir.flow <- rec.rate * i.num
dS <- -si.flow
dI <- si.flow - ir.flow
dR <- ir.flow
list(c(dS, dI, dR, si.flow, ir.flow), num = num)
})
}
接下来,定义损失函数,由于后续采用的是最小二乘,所以都是适用与回归的损失函数。
> mse <- function(infected, fit) {
+ sum((infected - fit)^2) / length(infected)
+ }
> r2 <- function(infected, fit) {
+ 1 - mse(infected, fit)/var(infected)
+ }
定义R0的拟合函数
> R0 <- function(days){
+
+ # 取窗口期内的数据拟合
+ WindowInfected <- infected[(days - window):(days - 1)]
+ # 持续天数
+ Days <- 1:(length(WindowInfected))
+
+ # 设置SIR模型的默认值,s.num易感人群,i.num已感人群,r.num已治愈人群
+ init <- c(s.num = N - WindowInfected[1], i.num = WindowInfected[1], r.num = 0)
+
+ # 定义损失函数
+ LOSS <- function(parameters) {
+ names(parameters) <- c("beta", "gamma")
+ out <- ode(y = init, times = Days, func = SIR, parms = parameters)
+ fit <- out[ , 3]
+ -r2(WindowInfected,fit)
+ }
+
+ # 拟合计算
+ Opt = optim(c(0.5, 0.5), LOSS, method = "L-BFGS-B", lower = c(0, 0), upper = c(Inf, 1))
+ Opt_par = setNames(Opt$par, c("beta", "gamma"))
+ data.frame(days = days,
+ R0 = Opt_par["beta"] / Opt_par["gamma"],
+ beta = Opt_par["beta"],
+ gamma = Opt_par["gamma"],
+ value = Opt$value,
+ date = ymd("2022-04-01") + days(startDay + days - 1) - 1) # StartDay - 1 | days - 1
+ }
从13个日期2022-04-18开始,对每一个时间进行拟合,计算R0值。
> # 找到需要计算的日期
> days<-(window+1):(length(infected));days
[1] 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46
[35] 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
[69] 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
> # 计算R0的计算
> RODF<-lapply(days,R0) %>% ldply
> head(RODF)
days R0 beta gamma value date
1 13 1.163701 0.5813041 0.4995306 -0.5091804 2022-04-18
2 14 1.115407 0.5574453 0.4997684 -0.7966765 2022-04-19
3 15 1.081334 0.5405033 0.4998486 -0.9677076 2022-04-20
4 16 1.070063 0.5348910 0.4998687 -0.9729603 2022-04-21
5 17 1.072671 0.5362001 0.4998738 -0.9679795 2022-04-22
6 18 1.065505 0.5326116 0.4998677 -0.9529303 2022-04-23
画图输出R0的预测值,从预测结果看,在5月初R0是最高点,是扩散最严重的时刻,北京市也是在4月底发紧急通知,封闭朝阳区的小区,并且5月份限制办公聚集,居家上班等强制干预行动,每天进行核酸检测。到6月初才放开跨区工作,逐步恢复工作秩序。
> plot(R0~date,data=RODF)
单独看一个R0的图并不明显,我们把累计确诊,每日新增确诊和R0值,合并在一起进行输出结果, 以x轴为时间统一对齐。
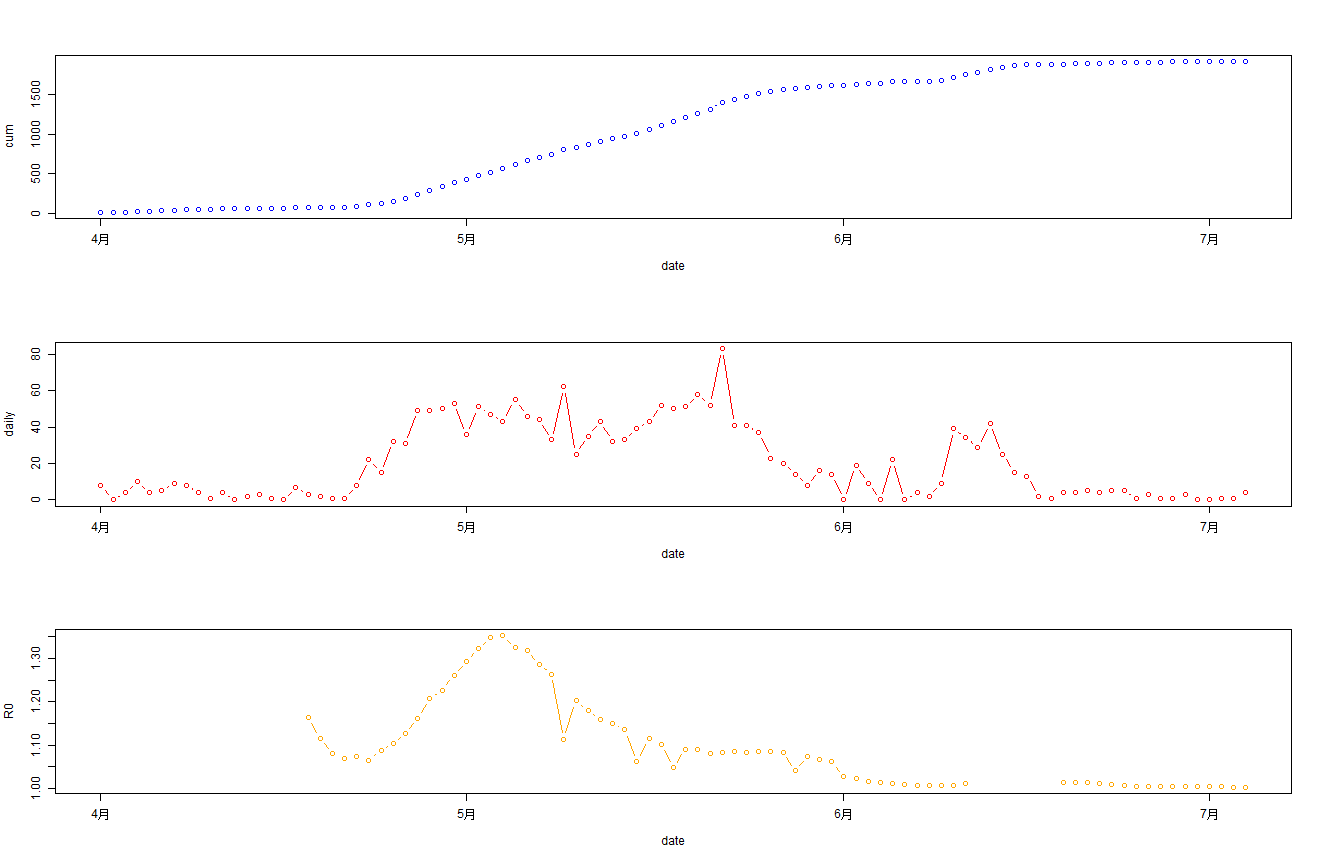
> par(mfrow = c(3, 1))
> plot(cum~date,data=bj202204,type='b',col="blue")
> plot(daily~date,data=bj202204,type='b',col="red")
>
> d2<-data.frame(date=RODF$date,R0=RODF$R0)
> d1<-data.frame(date=as.Date('2022-04-01')+0:16,R0=NA)
> d2<-rbind(d1,d2)
> plot(R0~date,data=d2,type='b',col="orange")
从2022年04月01日开始,最上面蓝色图为每日累计确诊病例,中间红色图为每日新增确诊,最下面橙色图为R0值。
通过观察R0值,很明显的能看到R0值在5月初达到顶点后,R0值开始大幅下降。从5月每日确诊人数来看趋势是平稳的,而且也在降低,因此说明北京本次防控是有效的。6月份逐步放开管制后,大家的工作和生活开始逐步恢复正常状态。
文本完整的代码,已经上传github,可以自由下载使用:https://github.com/bsspirit/infect/blob/main/code/beijing.r
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-coivd19-beijing